2.8 KiB
| title | date | description | featured | draft | toc | usePageBundles | codeLineNumbers | series | tags | comment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Removing and Recreating vCLS VMs | 2022-07-23T16:25:05-05:00 | How to remove and (optionally) recreate the vSphere Clustering Services VMs | false | true | true | true | false | Tips |
|
true |
Way back in 2020, VMware released vSphere 7 Update 1 and introduced the new vSphere Clustering Services (vCLS) to improve how cluster services like the Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS) operate. vCLS deploys lightweight agent VMs directly on the cluster being managed, and those VMs provide a decoupled and distributed control plane to offload some of the management responsibilities from the vCenter server.
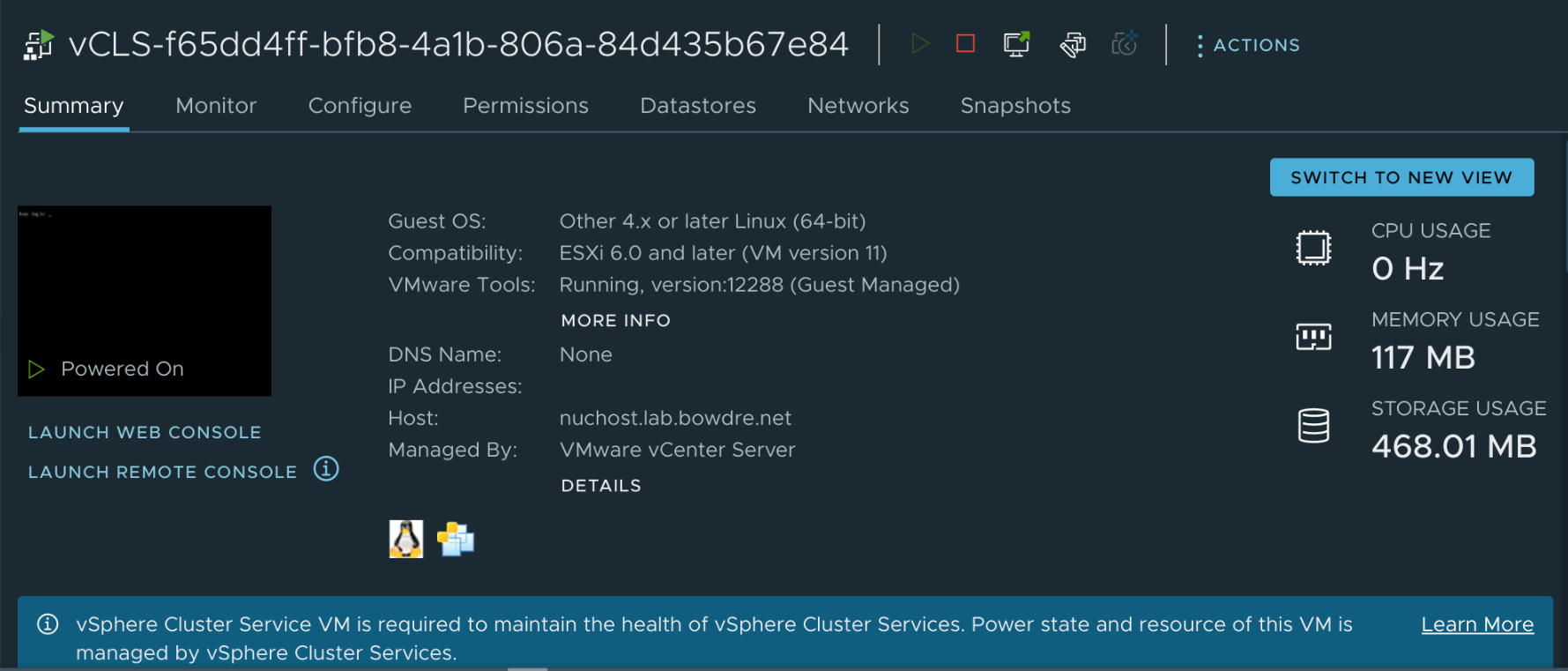
That's very cool, particularly in large continent-spanning environments or those which reach into multiple clouds, but it may not make sense to add those additional workloads in resource-constrained homelabs. And while the vCLS VMs are supposed to be automagically self-managed, sometimes things go a little wonky and that management fails to function correctly, which can negatively impact DRS. Recovering from such a scenario is complicated by the complete inability to manage the vCLS VMs through the vSphere UI.
Fortunately there's a somewhat-hidden way to disable (and re-enable) vCLS on a per-cluster basis, and it's easy to do once you know the trick. This can help if you want to permanently disable vCLS (like in a lab environment) or if you just need to turn it off and on again1 to clean up and redeploy uncooperative agent VMs.
Find the cluster's domain ID
It starts with determining the affected cluster's domain ID, which is very easy to do once you know where to look. Simply browse to the cluster object in your vSphere inventory, and look at the URL: