42 KiB
| title | date | draft | description | featured | toc | reply | categories | tags | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Building Proxmox Templates with Packer and GitHub Actions | 2024-06-12 | true | Using Packer, Vault, a GitHub Actions workflow, and self-hosted runners to automatically build VM templates for my Proxmox homelab. | false | true | true | Tips |
|
I've been using Proxmox in my homelab for a little while now, and I recently expanded the environment a bit with the addition of two HP Elite Mini 800 G9 computers. I figured it was time to start automating the process of building and maintaining my VM templates. I already had functional Packer templates for VMware so I used that content as a starting point for the Proxmox builds. Once I had the builds working locally, I just had to explore how to automate them.
This post will describe how I did it. It will cover a lot of the implementation details but may gloss over some general setup steps; you'll need at least passing familiarity with Packer and Vault to take this on.
Component Overview
There are a lot of parts to this setup, so let's start by quickly running through those:
- a Proxmox host to serve the virtual infrastructure and provide compute for the new templates,
- a Vault instance running in a container in the lab to hold the secrets needed for the builds,
- some Packer content for building the templates in the first place,
- an on-premise self-hosted GitHub runner to simplify connectivity between GitHub and my homelab,
- and a private GitHub repo to hold the code and tell the runner when it's time to get to work.
{{% notice note "Private Repo!" %}} GitHub strongly recommends that self-hosted runners only be used with private repositories.
This is because forks of your public repository can potentially run dangerous code on your self-hosted runner machine by creating a pull request that executes the code in a workflow.
I don't like the idea of randos running arbitrary code on my home infrastructure. So while I'm sharing my work publicly in this repo, the workflows there are disabled and there are no connected runners. I'm running my builds out of a private repo and recommend that you do the same. {{% /notice %}}
Proxmox Setup
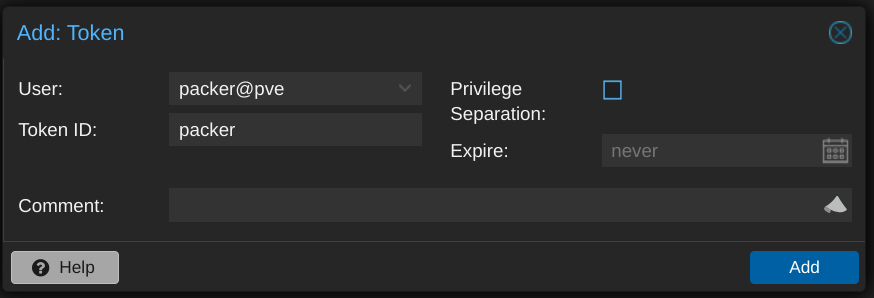
The only configuration I did on the Proxmox side of things was to create a user account that Packer could use. I called it packer but didn't set a password for it. Instead, I set up an API token for that account, making sure to uncheck the "Privilege Separation" box so that the token inherits the same permissions as the user itself.
To use the token, I needed the ID (in the form USERNAME@REALM!TOKENNAME) and the UUID-looking secret, which is only displayed once so I made sure to record it in a safe place.
Speaking of privileges, the Proxmox ISO integration documentation doesn't offer any details on the minimum required permissions, and none of my attempts worked until I eventually assigned the Administrator role to the packer user. (I plan on doing more testing to narrow the scope a bit before running this in production, but this will do for my homelab purposes.)
Otherwise I just needed to figure out the details like which network bridge, ISO storage, and VM storage the Packer-built VMs should use.
Vault Configuration
I use Vault to hold the configuration details for the template builds - not just traditional secrets like usernames and passwords, but basically every environment-specific setting as well. This approach lets others use my Packer code without having to change much (if any) of it; every value that I expect to change between environments is retrieved from Vault at run time.
Because this is just a homelab, I'm using Vault in Docker, and I'm making it available within my tailnet with Tailscale Serve using the following docker-compose.yaml
# torchlight! {"lineNumbers":true}
services:
tailscale:
image: tailscale/tailscale:latest
container_name: vault-tailscaled
restart: unless-stopped
environment:
TS_AUTHKEY: ${TS_AUTHKEY:?err}
TS_HOSTNAME: vault
TS_STATE_DIR: "/var/lib/tailscale/"
TS_SERVE_CONFIG: /config/serve-config.json
volumes:
- ./ts_data:/var/lib/tailscale/
- ./serve-config.json:/config/serve-config.json
vault:
image: hashicorp/vault
container_name: vault
restart: unless-stopped
environment:
VAULT_ADDR: 'https://0.0.0.0:8200'
cap_add:
- IPC_LOCK
volumes:
- ./data:/vault/data
- ./config:/vault/config
- ./log:/vault/log
command: vault server -config=/vault/config/vault.hcl
network_mode: "service:tailscale"
Vault's ./config/vault.hcl:
ui = true
listener "tcp" {
address = "0.0.0.0:8200"
tls_disable = "true"
}
storage "file" {
path = "/vault/data"
}
And Tailscale's ./serve-config.json:
# torchlight! {"lineNumbers":true}
{
"TCP": {
"443": {
"HTTPS": true
}
},
"Web": {
"vault.tailnet-name.ts.net:443": {
"Handlers": {
"/": {
"Proxy": "http://127.0.0.1:8200"
}
}
}
}
}
After performing the initial Vault setup, I then create a kv-v2 secrets engine for Packer to use:
vault secrets enable -path=packer kv-v2 # [tl! .cmd]
Success! Enabled the kv-v2 secrets engine at: packer/ # [tl! .nocopy]
And I define a policy which will grant the bearer read-only access to the data stored in the packer secrets as well as the ability to create and update its own token:
cat << EOF | vault policy write packer -
path "packer/*" {
capabilities = ["read", "list"]
}
path "auth/token/renew-self" {
capabilities = ["update"]
}
path "auth/token/create" {
capabilities = ["create", "update"]
}
EOF # [tl! .cmd:-12,1]
Success! Uploaded policy: packer2 # [tl! .nocopy]
Now I just need to create a token attached to the policy:
vault token create -policy=packer -no-default-policy
-orphan -ttl=4h -period=336h -display-name=packer # [tl! .cmd:-1,1 ]
Key Value # [tl! .nocopy:8]
--- -----
token hvs.CAES[...]GSFQ
token_accessor aleV[...]xu5I
token_duration 336h
token_renewable true
token_policies ["packer"]
identity_policies []
policies ["packer"]
Within the packer secrets engine, I have two secrets which each have a number of subkeys:
proxmox contains values related to the Proxmox environment:
| Key | Example value | Description |
|---|---|---|
api_url |
https://proxmox1.example.com:8006/api2/json |
URL to the Proxmox API |
insecure_connection |
true |
set to false if your Proxmox host has a valid certificate |
iso_path |
local:iso |
path for (existing) ISO storage |
iso_storage_pool |
local |
pool for storing created/uploaded ISOs |
network_bridge |
vmbr0 |
bridge the VM's NIC will be attached to |
node |
proxmox1 |
node name where the VM will be built |
token_id |
packer@pve!packer |
ID for an API token, in the form USERNAME@REALM!TOKENNAME |
token_secret |
3fc69f[...]d2077eda |
secret key for the token |
vm_storage_pool |
zfs-pool |
storage pool where the VM will be created |
linux holds values for the created VM template(s)
| Key | Example value | Description |
|---|---|---|
bootloader_password |
bootplease |
Grub bootloader password to set |
password_hash |
$6$rounds=4096$NltiNLKi[...]a7Shax41 |
hash of the build account's password (example generated with mkpasswd -m sha512crypt -R 4096) |
public_key |
ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC1[...]lXLUI5I40 admin@example.com |
SSH public key for the user |
username |
admin |
build account username |
Packer Content
The layout of my Packer Proxmox repo looks something like this:
.
├── .github # [tl! collapse:8 ]
│ ├── actions
│ │ └── packerbuild
│ │ ├── action.yml
│ │ ├── build.sh
│ │ └── Dockerfile
│ └── workflows
│ ├── build-single.yml
│ └── build.yml
├── builds
│ └── linux
│ └── ubuntu
│ ├── 22-04-lts
│ │ ├── data
│ │ │ ├── meta-data
│ │ │ └── user-data.pkrtpl.hcl
│ │ ├── hardening.sh
│ │ ├── linux-server.auto.pkrvars.hcl
│ │ ├── linux-server.pkr.hcl
│ │ └── variables.pkr.hcl
│ └── 24-04-lts # [tl! collapse:7 ]
│ ├── data
│ │ ├── meta-data
│ │ └── user-data.pkrtpl.hcl
│ ├── hardening.sh
│ ├── linux-server.auto.pkrvars.hcl
│ ├── linux-server.pkr.hcl
│ └── variables.pkr.hcl
├── certs
├── scripts
│ └── linux # [tl! collapse:16 ]
│ ├── cleanup-cloud-init.sh
│ ├── cleanup-packages.sh
│ ├── cleanup-subiquity.sh
│ ├── configure-pam_mkhomedir.sh
│ ├── configure-sshd.sh
│ ├── disable-multipathd.sh
│ ├── generalize.sh
│ ├── install-ca-certs.sh
│ ├── install-cloud-init.sh
│ ├── join-domain.sh
│ ├── persist-cloud-init-net.sh
│ ├── prune-motd.sh
│ ├── set-homedir-privacy.sh
│ ├── update-packages.sh
│ ├── wait-for-cloud-init.sh
│ └── zero-disk.sh
├── build.sh -> .github/actions/packerbuild/build.sh
└── vault-env.sh
.github/holds the actions and workflows that will perform the automated builds. I'll cover this later.builds/contains subfolders for OS types (Linux or Windows (eventually)) and then separate subfolders for each flavor.linux/ubuntu/22-04-lts/holds everything related to the Ubuntu 22.04 build:data/meta-datais an empty placeholder,data/user-data.pkrtpl.hclis a template file forcloud-initto perform the initial install,hardening.shis a script to perform basic security hardening,variables.pkr.hcldescribes all the variables for the build,linux-server.auto.pkrvars.hclassigns values to each of those variables, andlinux-server.pkr.hcldetails the steps for actually perfoming the build.
certs/is empty in my case but could contain CA certificates that need to be installed in the template.scripts/linux/contains a variety of scripts that will be executed by Packer as a part of the build.build.shis a (symlink to a) wrapper script which helps with running the builds locally.vault-env.shexports variables for connecting to my Vault instance for use bybuild.sh.
Input Variable Definitions
Let's take a quick look at the variable definitions in variables.pkr.hcl first. All it does is define the available variables along with their type, provide a brief description about what the variable should hold or be used for, and set sane defaults for some of them.
{{% notice note "Input Variables and Local Variables" %}} There are two types of variables used with Packer:
- Input Variables may have defined defaults, can be overridden, but cannot be changed after that initial override. They serve as build parameters, allowing aspects of the build to be altered without having to change the source code.
- Local Variables are useful for assigning a name to an expression. These expressions are evaluated at run time and can work with input variables, other local variables, data sources, and built-in functions.
Input variables are great for those predefined values, while local variables can be really handy for stuff that needs to be more dynamic. {{% /notice %}}
# torchlight! {"lineNumbers":true}
/*
Ubuntu Server 22.04 LTS variables using the Packer Builder for Proxmox.
*/
// BLOCK: variable
// Defines the input variables.
// Virtual Machine Settings
variable "remove_cdrom" {
type = bool
description = "Remove the virtual CD-ROM(s)."
default = true
}
variable "vm_name" {
type = string
description = "Name of the new template to create."
}
variable "vm_cpu_cores" {
type = number
description = "The number of virtual CPUs cores per socket. (e.g. '1')"
}
variable "vm_cpu_count" {
type = number
description = "The number of virtual CPUs. (e.g. '2')"
}
variable "vm_cpu_type" { # [tl! collapse:start]
type = string
description = "The virtual machine CPU type. (e.g. 'host')"
}
variable "vm_disk_size" {
type = string
description = "The size for the virtual disk (e.g. '60G')"
default = "60G"
}
variable "vm_bios_type" {
type = string
description = "The virtual machine BIOS type (e.g. 'ovmf' or 'seabios')"
default = "ovmf"
}
variable "vm_guest_os_keyboard" {
type = string
description = "The guest operating system keyboard input."
default = "us"
}
variable "vm_guest_os_language" {
type = string
description = "The guest operating system lanugage."
default = "en_US"
}
variable "vm_guest_os_timezone" {
type = string
description = "The guest operating system timezone."
default = "UTC"
}
variable "vm_guest_os_type" {
type = string
description = "The guest operating system type. (e.g. 'l26' for Linux 2.6+)"
}
variable "vm_mem_size" {
type = number
description = "The size for the virtual memory in MB. (e.g. '2048')"
}
variable "vm_network_model" {
type = string
description = "The virtual network adapter type. (e.g. 'e1000', 'vmxnet3', or 'virtio')"
default = "virtio"
}
variable "vm_scsi_controller" {
type = string
description = "The virtual SCSI controller type. (e.g. 'virtio-scsi-single')"
default = "virtio-scsi-single"
}
// VM Guest Partition Sizes
variable "vm_guest_part_audit" {
type = number
description = "Size of the /var/log/audit partition in MB."
}
variable "vm_guest_part_boot" {
type = number
description = "Size of the /boot partition in MB."
}
variable "vm_guest_part_efi" {
type = number
description = "Size of the /boot/efi partition in MB."
}
variable "vm_guest_part_home" {
type = number
description = "Size of the /home partition in MB."
}
variable "vm_guest_part_log" {
type = number
description = "Size of the /var/log partition in MB."
}
variable "vm_guest_part_root" {
type = number
description = "Size of the /var partition in MB. Set to 0 to consume all remaining free space."
default = 0
}
variable "vm_guest_part_swap" {
type = number
description = "Size of the swap partition in MB."
}
variable "vm_guest_part_tmp" {
type = number
description = "Size of the /tmp partition in MB."
}
variable "vm_guest_part_var" {
type = number
description = "Size of the /var partition in MB."
}
variable "vm_guest_part_vartmp" {
type = number
description = "Size of the /var/tmp partition in MB."
}
// Removable Media Settings
variable "cd_label" {
type = string
description = "CD Label"
default = "cidata"
}
variable "iso_checksum_type" {
type = string
description = "The checksum algorithm used by the vendor. (e.g. 'sha256')"
}
variable "iso_checksum_value" {
type = string
description = "The checksum value provided by the vendor."
}
variable "iso_file" {
type = string
description = "The file name of the ISO image used by the vendor. (e.g. 'ubuntu-<version>-live-server-amd64.iso')"
}
variable "iso_url" {
type = string
description = "The URL source of the ISO image. (e.g. 'https://mirror.example.com/.../os.iso')"
}
// Boot Settings
variable "vm_boot_command" {
type = list(string)
description = "The virtual machine boot command."
default = []
}
variable "vm_boot_wait" {
type = string
description = "The time to wait before boot."
}
// Communicator Settings and Credentials
variable "build_remove_keys" {
type = bool
description = "If true, Packer will attempt to remove its temporary key from ~/.ssh/authorized_keys and /root/.ssh/authorized_keys"
default = true
}
variable "communicator_insecure" {
type = bool
description = "If true, do not check server certificate chain and host name"
default = true
}
variable "communicator_port" {
type = string
description = "The port for the communicator protocol."
}
variable "communicator_ssl" {
type = bool
description = "If true, use SSL"
default = true
}
variable "communicator_timeout" {
type = string
description = "The timeout for the communicator protocol."
}
// Provisioner Settings
variable "cloud_init_apt_packages" {
type = list(string)
description = "A list of apt packages to install during the subiquity cloud-init installer."
default = []
}
variable "cloud_init_apt_mirror" {
type = string
description = "Sets the default apt mirror during the subiquity cloud-init installer."
default = ""
}
variable "post_install_scripts" {
type = list(string)
description = "A list of scripts and their relative paths to transfer and run after OS install."
default = []
}
variable "pre_final_scripts" {
type = list(string)
description = "A list of scripts and their relative paths to transfer and run before finalization."
default = []
} # [tl! collapse:end]
(Collapsed because I think you get the idea, but feel free to expand to view the whole thing.)
Input Variable Assignments
Now that I've told Packer about what variables I intend to use, I can then go about setting values for those variables. That's done in the linux-server.auto.pkrvars.hcl file.
# torchlight! {"lineNumbers":true}
/*
Ubuntu Server 22.04 LTS variables used by the Packer Builder for Proxmox.
*/
// Guest Operating System Metadata
vm_guest_os_keyboard = "us"
vm_guest_os_language = "en_US"
vm_guest_os_timezone = "America/Chicago"
// Virtual Machine Guest Operating System Setting
vm_guest_os_type = "l26"
//Virtual Machine Guest Partition Sizes (in MB)
vm_guest_part_audit = 4096 # [tl! **:9 ~~:9]
vm_guest_part_boot = 512
vm_guest_part_efi = 512
vm_guest_part_home = 8192
vm_guest_part_log = 4096
vm_guest_part_root = 0
vm_guest_part_swap = 1024
vm_guest_part_tmp = 4096
vm_guest_part_var = 8192
vm_guest_part_vartmp = 1024
// Virtual Machine Hardware Settings
vm_cpu_cores = 1 # [tl! **:8 ~~:8]
vm_cpu_count = 2
vm_cpu_type = "host"
vm_disk_size = "60G" #
vm_bios_type = "ovmf"
vm_mem_size = 2048 #
vm_name = "Ubuntu2204"
vm_network_card = "virtio"
vm_scsi_controller = "virtio-scsi-single"
// Removable Media Settings
iso_checksum_type = "sha256" # [tl! **:3 ~~:3]
iso_checksum_value = "45f873de9f8cb637345d6e66a583762730bbea30277ef7b32c9c3bd6700a32b2" #
iso_file = "ubuntu-22.04.4-live-server-amd64.iso"
iso_url = "https://releases.ubuntu.com/jammy/ubuntu-22.04.4-live-server-amd64.iso"
remove_cdrom = true
// Boot Settings
boot_key_interval = "250ms"
vm_boot_wait = "4s"
vm_boot_command = [ # [tl! **:8 ~~:8]
"<esc><wait>c",
"linux /casper/vmlinuz --- autoinstall ds=\"nocloud\"",
"<enter><wait5s>",
"initrd /casper/initrd",
"<enter><wait5s>",
"boot",
"<enter>"
]
// Communicator Settings
communicator_port = 22
communicator_timeout = "25m"
// Provisioner Settings
cloud_init_apt_packages = [ # [tl! **:7 ~~:7]
"cloud-guest-utils",
"net-tools",
"perl",
"qemu-guest-agent",
"vim",
"wget"
]
post_install_scripts = [ # [tl! **:9 ~~:9]
"scripts/linux/wait-for-cloud-init.sh",
"scripts/linux/cleanup-subiquity.sh",
"scripts/linux/install-ca-certs.sh",
"scripts/linux/disable-multipathd.sh",
"scripts/linux/prune-motd.sh",
"scripts/linux/persist-cloud-init-net.sh",
"scripts/linux/configure-pam_mkhomedir.sh",
"scripts/linux/update-packages.sh"
]
pre_final_scripts = [ # [tl! **:6 ~~:6]
"scripts/linux/cleanup-cloud-init.sh",
"scripts/linux/cleanup-packages.sh",
"builds/linux/ubuntu/22-04-lts/hardening.sh",
"scripts/linux/zero-disk.sh",
"scripts/linux/generalize.sh"
]
As you can see, this sets up a lot of the properties which aren't strictly environment specific, like:
- partition sizes (ll. 14-23),
- virtual hardware settings (ll. 26-34),
- the hash and URL for the installer ISO (ll. 37-40),
- the command to be run at first boot to start the installer in unattended mode (ll. 47-53),
- a list of packages to install during the
cloud-initinstall phase, primarily the sort that might be needed during later steps (ll. 62-67), - a list of scripts to execute after
cloud-init(ll. 71-78), - and a list of scripts to run at the very end of the process (ll. 82-86).
We'll look at the specifics of those scripts shortly, but first...
Packer Build File
Let's explore the Packer build file, linux-server.pkr.hcl, which is the set of instructions used by Packer for performing the deployment. It's what ties everything else together.
This one is kind of complex so we'll take it a block or two at a time.
It starts by setting the required minimum version of Packer and identifying what plugins (and versions) will be used to perform the build. I'm using the Packer plugin for Proxmox for executing the build on Proxmox (duh), and the Packer SSH key plugin to simplify handling of SSH keys (we'll see how in the next block).
# torchlight! {"lineNumbers":true}
/*
Ubuntu Server 22.04 LTS template using the Packer Builder for Proxmox.
*/
// BLOCK: packer
// The Packer configuration.
packer {
required_version = ">= 1.9.4" # [tl! ** ~~]
required_plugins {
proxmox = { # [tl! **:2 ~~:2]
version = ">= 1.1.8"
source = "github.com/hashicorp/proxmox"
}
ssh-key = { # [tl! **:2 ~~:2]
version = "= 1.0.3"
source = "github.com/ivoronin/sshkey"
}
}
}
This bit creates the sshkey data resource which uses the SSH plugin to generate a new SSH keypair to be used during the build process:
# torchlight! {"lineNumbers":true, "lineNumbersStart":22}
// BLOCK: locals
// Defines the local variables.
// Dynamically-generated SSH key
data "sshkey" "install" { # [tl! **:2 ~~:2]
type = "ed25519"
name = "packer_key"
}
This first set of locals {} blocks take advantage of the dynamic nature of local variables. They call the vault function to retrieve secrets from Vault and hold them as local variables. It's broken into a section for "standard" variables, which just hold configuration information like URLs and usernames, and one for "sensitive" variables like passwords and API tokens. The sensitive ones get sensitive = true to make sure they won't be printed in the logs anywhere.
# torchlight! {"lineNumbers":true, "lineNumbersStart":31}
////////////////// Vault Locals //////////////////
// To retrieve secrets from Vault, the following environment variables MUST be defined:
// - VAULT_ADDR : base URL of the Vault server ('https://vault.example.com/')
// - VAULT_NAMESPACE : namespace path to where the secrets live ('organization/sub-org', only for Vault Enterprise)
// - VAULT_TOKEN : token ID with rights to read/list
//
// Syntax for the vault() call:
// vault("SECRET_ENGINE/data/SECRET_NAME", "KEY")
//
// Standard configuration values:
locals { # [tl! **:10]
build_public_key = vault("packer/data/linux", "public_key") // SSH public key for the default admin account
build_username = vault("packer/data/linux", "username") // Username for the default admin account
proxmox_url = vault("packer/data/proxmox", "api_url") // Proxmox API URL
proxmox_insecure_connection = vault("packer/data/proxmox", "insecure_connection") // Allow insecure connections to Proxmox
proxmox_node = vault("packer/data/proxmox", "node") // Proxmox node to use for the build
proxmox_token_id = vault("packer/data/proxmox", "token_id") // Proxmox token ID
proxmox_iso_path = vault("packer/data/proxmox", "iso_path") // Path to the ISO storage
proxmox_vm_storage_pool = vault("packer/data/proxmox", "vm_storage_pool") // Proxmox storage pool to use for the build
proxmox_iso_storage_pool = vault("packer/data/proxmox", "iso_storage_pool") // Proxmox storage pool to use for the ISO
proxmox_network_bridge = vault("packer/data/proxmox", "network_bridge") // Proxmox network bridge to use for the build
}
// Sensitive values:
local "bootloader_password"{ # [tl! **:10]
expression = vault("packer/data/linux", "bootloader_password") // Password to set for the bootloader
sensitive = true
}
local "build_password_hash" {
expression = vault("packer/data/linux", "password_hash") // Password hash for the default admin account
sensitive = true
}
local "proxmox_token_secret" {
expression = vault("packer/data/proxmox", "token_secret") // Token secret for authenticating to Proxmox
sensitive = true
}
////////////////// End Vault Locals //////////////////
And the next locals {} block leverages other expressions to:
- dynamically set
local.build_dateto the current time (l. 70), - combine individual string variables, like
local.iso_checksumandlocal.iso_path(ll. 73-74), - define a shutdown command to clean up sudoers includes and shutdown the VM at the end of the build (ll. 75),
- capture the keypair generated by the SSH key plugin (ll. 76-77),
- and use the []
templatefile()function](https://developer.hashicorp.com/packer/docs/templates/hcl_templates/functions/file/templatefile) to process thecloud-initconfig file and insert appropriate variables (ll. 78-101)
# torchlight! {"lineNumbers":true, "lineNumbersStart":69}
locals {
build_date = formatdate("YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm ZZZ", timestamp()) # [tl! ** ~~]
build_description = "Ubuntu Server 22.04 LTS template\nBuild date: ${local.build_date}\nBuild tool: ${local.build_tool}"
build_tool = "HashiCorp Packer ${packer.version}"
iso_checksum = "${var.iso_checksum_type}:${var.iso_checksum_value}" # [tl! **:2 ~~:2]
iso_path = "${local.proxmox_iso_path}/${var.iso_file}"
shutdown_command = "sudo sh -c 'rm -f /etc/sudoers.d/*; /usr/sbin/shutdown -P now'"
ssh_private_key_file = data.sshkey.install.private_key_path # [tl! **:1 ~~:1]
ssh_public_key = data.sshkey.install.public_key
data_source_content = { # [tl! **:23]
"/meta-data" = file("${abspath(path.root)}/data/meta-data")
"/user-data" = templatefile("${abspath(path.root)}/data/user-data.pkrtpl.hcl", { # [tl! **:20 ~~:20]
apt_mirror = var.cloud_init_apt_mirror
apt_packages = var.cloud_init_apt_packages
build_password_hash = local.build_password_hash
build_username = local.build_username
ssh_keys = concat([local.ssh_public_key], [local.build_public_key])
vm_guest_os_hostname = var.vm_name
vm_guest_os_keyboard = var.vm_guest_os_keyboard
vm_guest_os_language = var.vm_guest_os_language
vm_guest_os_timezone = var.vm_guest_os_timezone
vm_guest_part_audit = var.vm_guest_part_audit
vm_guest_part_boot = var.vm_guest_part_boot
vm_guest_part_efi = var.vm_guest_part_efi
vm_guest_part_home = var.vm_guest_part_home
vm_guest_part_log = var.vm_guest_part_log
vm_guest_part_root = var.vm_guest_part_root
vm_guest_part_swap = var.vm_guest_part_swap
vm_guest_part_tmp = var.vm_guest_part_tmp
vm_guest_part_var = var.vm_guest_part_var
vm_guest_part_vartmp = var.vm_guest_part_vartmp
})
}
}
The source {} block is where we get to the meat of the operation. This matches the input and local variables to the Packer options that tell it:
- how to connect and authenticate to the Proxmox host (ll. 110-113, 116),
- what virtual hardware settings the VM should have (ll. 119-141),
- that
local.data_source_content(which contains the renderedcloud-initconfiguration) should be mounted as a virtual CD-ROM device (ll. 144-149), - to download and verify the installer ISO from
var.iso_url, save it tolocal.proxmox_iso_storage_pool, and mount it as the primary CD-ROM device (ll. 150-155), - what command to run at boot to start the install process (l. 159),
- and how to communicate with the VM once the install is under way (ll. 163-168).
# torchlight! {"lineNumbers":true, "lineNumbersStart":104}
// BLOCK: source
// Defines the builder configuration blocks.
source "proxmox-iso" "linux-server" {
// Proxmox Endpoint Settings and Credentials
insecure_skip_tls_verify = local.proxmox_insecure_connection # [tl! **:3 ~~:3]
proxmox_url = local.proxmox_url
token = local.proxmox_token_secret
username = local.proxmox_token_id
// Node Settings
node = local.proxmox_node # [tl! ** ~~]
// Virtual Machine Settings
bios = "ovmf" # [tl! **:22 ~~:22]
cores = var.vm_cpu_cores
cpu_type = var.vm_cpu_type
memory = var.vm_mem_size
os = var.vm_guest_os_type
scsi_controller = var.vm_scsi_controller
sockets = var.vm_cpu_count
template_description = local.build_description
template_name = var.vm_name
vm_name = var.vm_name
disks {
disk_size = var.vm_disk_size
storage_pool = local.proxmox_vm_storage_pool
}
efi_config {
efi_storage_pool = local.proxmox_vm_storage_pool
efi_type = "4m"
pre_enrolled_keys = true
}
network_adapters {
bridge = local.proxmox_network_bridge
model = var.vm_network_model
}
// Removable Media Settings
additional_iso_files {
cd_content = local.data_source_content
cd_label = var.cd_label
iso_storage_pool = local.proxmox_iso_storage_pool
unmount = var.remove_cdrom
}
iso_checksum = local.iso_checksum
// iso_file = local.iso_path
iso_url = var.iso_url
iso_download_pve = true
iso_storage_pool = local.proxmox_iso_storage_pool
unmount_iso = var.remove_cdrom
// Boot and Provisioning Settings
boot_command = var.vm_boot_command
boot_wait = var.vm_boot_wait
// Communicator Settings and Credentials
communicator = "ssh"
ssh_clear_authorized_keys = var.build_remove_keys
ssh_port = var.communicator_port
ssh_private_key_file = local.ssh_private_key_file
ssh_timeout = var.communicator_timeout
ssh_username = local.build_username
}
// BLOCK: build // Defines the builders to run, provisioners, and post-processors.
build { sources = [ "source.proxmox-iso.linux-server" ]
provisioner "file" { source = "certs" destination = "/tmp" }
provisioner "file" { source = "scripts/linux/join-domain.sh" destination = "/home/${local.build_username}/join-domain.sh" }
provisioner "shell" { execute_command = "bash {{ .Path }}" expect_disconnect = true scripts = formatlist("${path.cwd}/%s", var.post_install_scripts) }
provisioner "shell" { env = { "BOOTLOADER_PASSWORD" = local.bootloader_password } execute_command = "{{ .Vars }} bash {{ .Path }}" expect_disconnect = true pause_before = "30s" scripts = formatlist("${path.cwd}/%s", var.pre_final_scripts) } }
#### `cloud-init` Config
Now let's drill into that `cloud-init` template file, `builds/linux/ubuntu/22-04-lts/data/user-data.pkrtpl.hcl`. It follows the basic YAML-based syntax of a standard [cloud config file](https://cloudinit.readthedocs.io/en/latest/reference/examples.html), but with some [HCL templating](https://developer.hashicorp.com/packer/docs/templates/hcl_templates/functions/file/templatefile) to pull in certain values from elsewhere.
```yaml
# torchlight! {"lineNumbers":true}
#cloud-config
autoinstall:
%{ if length( apt_mirror ) > 0 ~}
apt:
primary:
- arches: [default]
uri: "${ apt_mirror }"
%{ endif ~}
early-commands: # [tl! **:5]
- sudo systemctl stop ssh # [tl! ~~]
identity:
hostname: ${ vm_guest_os_hostname } # [tl! ~~:2]
password: '${ build_password_hash }'
username: ${ build_username }
keyboard:
layout: ${ vm_guest_os_keyboard }
late-commands: # [tl! **:2]
- echo "${ build_username } ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL" > /target/etc/sudoers.d/${ build_username } # [tl! ~~:1]
- curtin in-target --target=/target -- chmod 400 /etc/sudoers.d/${ build_username }
locale: ${ vm_guest_os_language }
network: # [tl! collapse:9]
network:
version: 2
ethernets:
mainif:
match:
name: e*
critical: true
dhcp4: true
dhcp-identifier: mac
%{ if length( apt_packages ) > 0 ~} # [tl! **:5]
packages:
%{ for package in apt_packages ~} # [tl! ~~:2]
- ${ package }
%{ endfor ~}
%{ endif ~}
ssh:
install-server: true
allow-pw: true
%{ if length( ssh_keys ) > 0 ~} # [tl! **:5]
authorized-keys:
%{ for ssh_key in ssh_keys ~} # [tl! ~~2]
- ${ ssh_key }
%{ endfor ~}
%{ endif ~}
storage:
config: # [tl! collapse:start]
- ptable: gpt
path: /dev/sda
wipe: superblock
type: disk
id: disk-sda
- device: disk-sda
size: ${ vm_guest_part_efi }M
wipe: superblock
flag: boot
number: 1
grub_device: true
type: partition
id: partition-0
- fstype: fat32
volume: partition-0
label: EFIFS
type: format
id: format-efi
- device: disk-sda
size: ${ vm_guest_part_boot }M
wipe: superblock
number: 2
type: partition
id: partition-1
- fstype: xfs
volume: partition-1
label: BOOTFS
type: format
id: format-boot
- device: disk-sda
size: -1
wipe: superblock
number: 3
type: partition
id: partition-2
- name: sysvg
devices:
- partition-2
type: lvm_volgroup
id: lvm_volgroup-0
- name: home
volgroup: lvm_volgroup-0
size: ${ vm_guest_part_home}M
wipe: superblock
type: lvm_partition
id: lvm_partition-home
- fstype: xfs
volume: lvm_partition-home
type: format
label: HOMEFS
id: format-home
- name: tmp
volgroup: lvm_volgroup-0
size: ${ vm_guest_part_tmp }M
wipe: superblock
type: lvm_partition
id: lvm_partition-tmp
- fstype: xfs
volume: lvm_partition-tmp
type: format
label: TMPFS
id: format-tmp
- name: var
volgroup: lvm_volgroup-0
size: ${ vm_guest_part_var }M
wipe: superblock
type: lvm_partition
id: lvm_partition-var
- fstype: xfs
volume: lvm_partition-var
type: format
label: VARFS
id: format-var
- name: log
volgroup: lvm_volgroup-0
size: ${ vm_guest_part_log }M
wipe: superblock
type: lvm_partition
id: lvm_partition-log
- fstype: xfs
volume: lvm_partition-log
type: format
label: LOGFS
id: format-log
- name: audit
volgroup: lvm_volgroup-0
size: ${ vm_guest_part_audit }M
wipe: superblock
type: lvm_partition
id: lvm_partition-audit
- fstype: xfs
volume: lvm_partition-audit
type: format
label: AUDITFS
id: format-audit
- name: vartmp
volgroup: lvm_volgroup-0
size: ${ vm_guest_part_vartmp }M
wipe: superblock
type: lvm_partition
id: lvm_partition-vartmp
- fstype: xfs
volume: lvm_partition-vartmp
type: format
label: VARTMPFS
id: format-vartmp
- name: root
volgroup: lvm_volgroup-0
%{ if vm_guest_part_root == 0 ~}
size: -1
%{ else ~}
size: ${ vm_guest_part_root }M
%{ endif ~}
wipe: superblock
type: lvm_partition
id: lvm_partition-root
- fstype: xfs
volume: lvm_partition-root
type: format
label: ROOTFS
id: format-root
- path: /
device: format-root
type: mount
id: mount-root
- path: /boot
device: format-boot
type: mount
id: mount-boot
- path: /boot/efi
device: format-efi
type: mount
id: mount-efi
- path: /home
device: format-home
type: mount
id: mount-home
- path: /tmp
device: format-tmp
type: mount
id: mount-tmp
- path: /var
device: format-var
type: mount
id: mount-var
- path: /var/log
device: format-log
type: mount
id: mount-log
- path: /var/log/audit
device: format-audit
type: mount
id: mount-audit
- path: /var/tmp
device: format-vartmp
type: mount
id: mount-vartmp # [tl! collapse:end]
user-data:
package_upgrade: true
disable_root: true
timezone: ${ vm_guest_os_timezone }
version: 1
Some of the key tasks handled by this configuration include:
- stopping the SSH server (l. 10),
- setting the hostname (l 12), inserting username and password (ll. 13-14),
- enabling (temporary) passwordless-sudo (ll. 17-18),
- installing a templated list of packages (ll. 30-35),
- inserting a templated list of SSH public keys (ll. 39-44),
- and other needful things like setting up drive partitioning.
cloud-init will reboot the VM once it completes, and when it comes back online it will have a DHCP-issued IP address and the accounts/credentials needed for Packer to log in via SSH and continue the setup.